SafeSwap is a revolutionary atomic swap platform that enables tokens to transfer between different blockchains.
SafeSwap is using state-of-the-art technology and is completely decentralized without the use of a third party.
What is an Atomic Swap?
An atomic swap is an exchange of cryptocurrencies from separate blockchains. The swap is conducted between two entities without a third party’s involvement. The idea is to remove centralized intermediaries like regulated exchanges and give token owners total control.
The term atomic derives from the term “atomic state” in which a state has no substates; it either happens or it doesn’t—there is no other alternative. This refers to the state of the cryptocurrency transaction; it happens or it doesn’t.
Most atomic swap-enabled wallets and blockchains use smart contracts. Smart contracts are programs within blockchains that execute when certain conditions are met. In this case, the conditions are that each party agrees to the transaction before a timer runs out. Using a smart contract in the trade prevents either party from stealing a cryptocurrency from the other.

How to do an Atomic Swap?
It is done using cryptocurrency wallets and Hash Timelock Contracts (HTLC), which enforce the exchange when both parties agree to it. In reality, there are only a few atomic swap wallet providers and decentralized exchanges that can be used in a swap.
Understanding Atomic Swaps
Each cryptocurrency is backed by a blockchain, and this limits the project to use only one blockchain as they depend on their token being on that blockchain. For example, VET has a blockchain called vechain, and ETH (Ether) has another. That means if you have a project on vechain, users need to buy your token on vechain in order to use your product. If you deploy your token contract on multiple blockchains, you can also deploy your smart contracts (which your product uses) on these blockchains, allowing an Ether user to use your product on the Ether chain. Atomic swaps allow you to exchange tokens from different blockchains in one trade.
The technicals of SafeSwap’s Atomic Swap Process
In an atomic swap, an owner agree to exchange their tokens he agree on. The smart contract program sees that the owner agreed to it, so it executes the trade. The transaction is recorded in the blockchain and validated by the network nodes, and then a new block is opened for another transaction.
The transaction cannot be reversed. The owner must agree to another transaction to exchange the tokens again if they would like them back.
Atomic swaps use Hash Timelock Contracts (HTLC) to automate the exchange of tokens. As its name denotes, HTLC is a time-bound smart contract between parties that involves generating one cryptographic hash on each end.
A cryptographic hash function is an algorithm that converts data of variable length, such as a person’s wallet address and transaction information. It converts it to a hexadecimal number with a fixed length. In general, the number that is generated is called the hash.
HTLC requires the owner to acknowledge receipt of funds within a specified timeframe. If the owner fails to confirm the transaction within the timeframe, then the entire transaction is voided, and funds can be reclaimed. This eliminates counterparty risk, or the risk that the owner will accept the offered coins and decline the transfer of their coins.
For instance, suppose Bob wants to convert 10,000 SHA on vechain to the same amount on Ethereum. He submits the transaction through an atomic swap. A cryptographic hash function generates a hex number to encrypt the transaction during this process.
Bob needs to unlock his respective funds using their encrypted numbers. He have to do this within a specified timeframe, or the transfer will not occur. The HTLC within the blockchains then executes the trade.
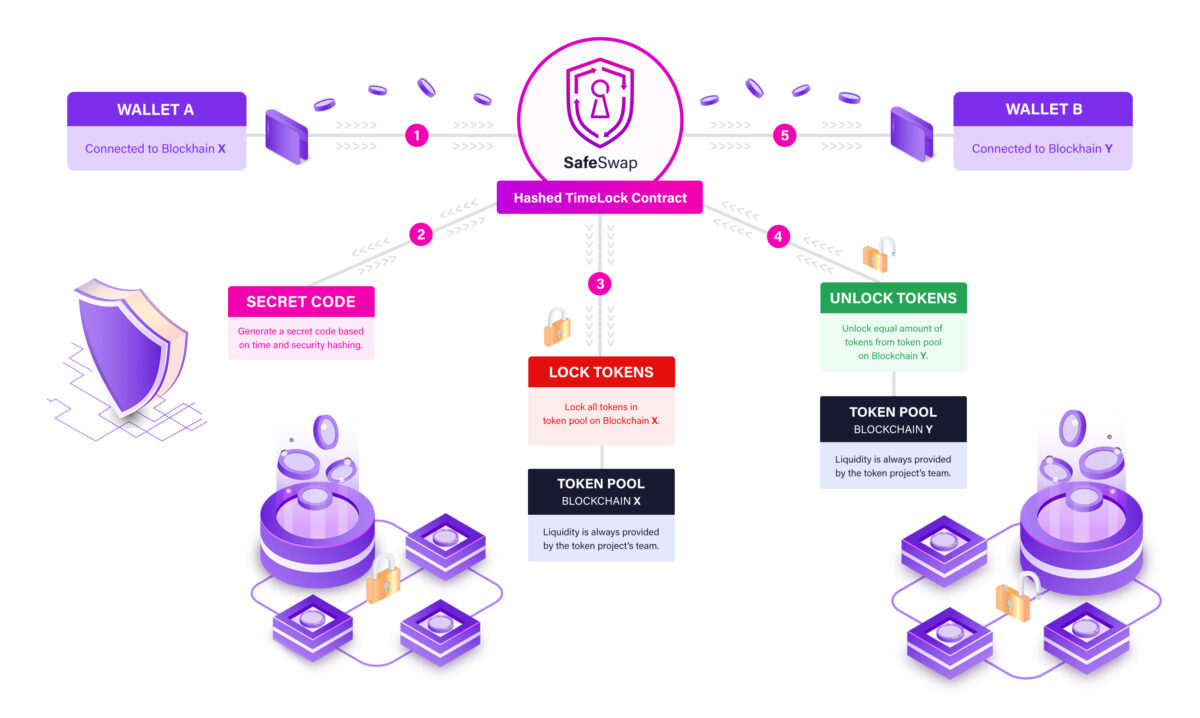
SafeSwap’s Atomic Swapping Process
1. Initiate
In order to initiate a swap, the user must select a blockchain, connect a wallet, select the preferred token and fill in the amount to swap.
2. Secure
SafeSwap’s integrated UI then creates a unique secret code which delivers hash data to the contract.
3. Lock
If a swap is initiated, SafeSwap will lock all tokens received from the source wallet in the related token pool on the source blockchain.
4. Unlock
SafeSwap accounts for the required tokens necessary and uses the unique code to unlock tokens on the destination blockchain.
5. Claim
The tokens are then transferred to the connected destination wallet.
Back to newsBlockchain Project Owner?
SafeSwap V1 will be supporting EVM chains like vechain, Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain and Polygon/Matic. If you’re a blockchain project owner and you’re feeling the need to take your project cross-chain, get in touch with us via our contact page, we might be able to help each other out and add value to each other’s project!
 Nederlands
Nederlands Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français